Oftentimes we have brilliant ideas which remain unexecuted due to lack of financial support or a business plan. While ideating is exhilarating, the execution of these ideas with respect to administrative requirements and financial constraints can be quite daunting. Hence, converting an ‘idea’ into a ‘business’ will require adequate investment at every stage.
In view of the above, we aim to bring some clarity to our future and existing entrepreneurs regarding stages of business and the sources of funding to match their needs. While these funding requirements would change depending on the type of business/industry/labour requirement, we are trying to present a more generic view, usable by most start-ups generally.
Let’s start with the basics!
Types of Funding
- Equity; and
- Debt.
Equity refers to the infused capital by the Promoters or Owners themselves, while Debt is the borrowed money either from banks or relatives.
While evaluating whether one must go for debt or equity, the Promoters must consider the cost of the funding and related risks or benefits. Debt is cheap and involves only payment of interest, for which one may avail tax benefits. When the company does well, the interest cost remains fixed, thereby resulting in more gains for the Promoters. However, companies have to create a charge on their assets, and more debt may result in over-leveraging and increase in cost. Moreover, debt is riskier for the company, as it needs to be serviced whether or not the company makes profits. Hence, if the quantum of debt availed by the company is adequate and at lower rates, it is beneficial to the company, and can even aid in enhancing the company’s return on equity through leveraging.
Equity funding can be sourced through own funds, relative’s contributions and investors. Equity is relatively risk-free in the terms that the company is obliged to declare dividends only when it is making profits. However, investors will ask for shares in the company, thereby diluting the Promoters’ decision-making abilities. They may or may not share the same vision as the Promoters, and their profit-making motives could be short term. Therefore, choosing the right kind of investors – Angel, PE, Venture Capital, is key.
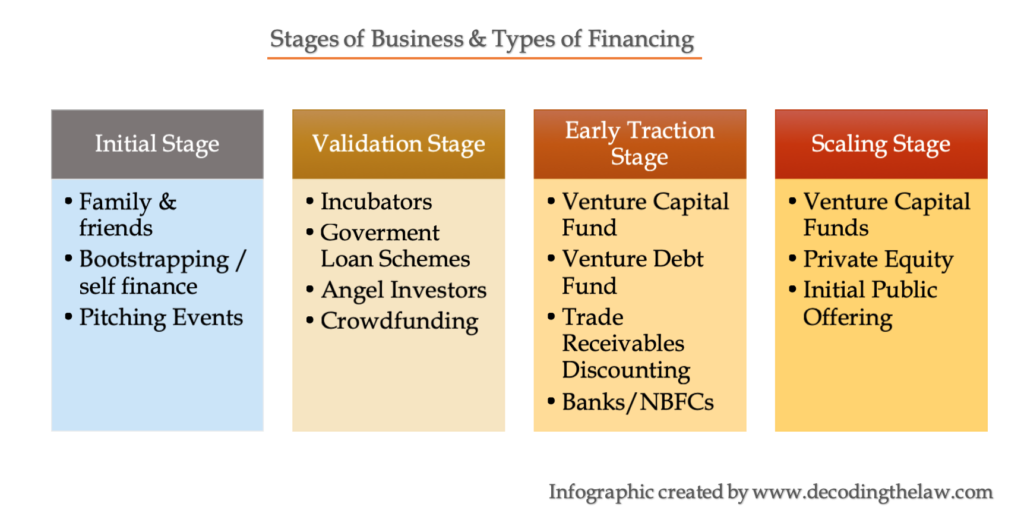
Hence, once you believe you do have a marketable idea, you must chart out its’ growth scheme by learning about demand patterns, market trends and your ability to create value by bringing your brand to the market. You must draw up a budget plan entailing the fixed costs (one-time costs) and operating costs expected to be incurred. While carrying out the above exercise, it is recommended that the promoters seek expert help from tax experts, marketing agencies and lawyers, so that they can focus on growing the idea while receiving the best possible support to enable them to do so.
Following are some examples of initiatives by the State:
Karnataka:
The government of Karanataka has set up a portal known as startup.karnataka.gov.in which enables start-ups to find incubators and funding. The Start-Up Policy of Karanataka has launched an ‘Idea2PoC’ scheme, which is given in the form of a one-time grant-in-aid of up to Rs. 50 lakhs. Applications can be made through their online portal.
Gujarat:
The government of Gujarat provides seed funding to startups in the form of sustenance allowance, product development assistance and marketing assistance. An amount of Rs. 10 lakhs is provided as seed funding under the Electronics & IT/ITeS Start-up Policy (2016-21).
Rajasthan:
Under the Rajasthan Startup Policy 2015, entrepreneurs are being provided with provides seed funding in form of monthly sustenance allowance under the ‘Assistance for Startup at Idea or prototype stage’. All eligible startups can apply for seed funding through their iStart Startup dashboard.
More information about government schemes for start-ups is available at www.startupindia.gov.in
Hence, entrepreneurs must focus on creating value in the market through their innovation or services. During their validation or growth stages, the promoters and their core team must apply their best efforts to let their product shine. A solid foundation of robust financial backing, strong compliance regime and economical business processes to support your work will help to deliver high quality products or services, and that is the only way to strong, long-term, assured and sustainable growth.
Key take-aways:
- Entrepreneurs must spend considerable time evaluating the best business form for themselves – company, partnership, LLP, sole proprietorship;
- Entrepreneurs must seek help of experts to formulate their business and marketing plans (while planning their sources of funding at various stages);
- They can set 5-year plans for their venture, to ensure growth is scaled as per the amount of time and resources applied;
- Seek expert help;
- Look out for government schemes that support your ideas; and
- Focus on creating value and long-term growth, instead of short-term profits.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


